time:2025-08-27 source:锂电产学研
01 Main suppliers
1. Japanese companies (leading in technology)
DNP (Greater Japan Printing): The world's largest market share (about 50%), with deep technological accumulation and high product stability.
Showa Denko: The world's second-largest supplier known for its high barrier properties and electrolyte resistance.
T&T E-Materials: a joint venture between Toyo Aluminum and letterpress printing, focusing on high-performance aluminum-plastic films.
2. Korean companies
Soulbrain: The largest supplier in South Korea, with a high market share in the field of power batteries and outstanding cost-effectiveness.
Daeduck GDS: Focusing on the high-end market, our products are used in consumer electronics and power batteries.
3. Chinese enterprises (accelerated localization)
Xinlun New Materials: Acquired Japanese T&T, localized technology, customers include CATL, etc.
Daoming Optics: Breakthrough in self-developed technology, mass production of aluminum-plastic film for power batteries.
Zijiang New Materials: Mainly in the field of consumer electronics, expanding towards power batteries.
Putailai (subsidiary Zhuoli): Layout aluminum-plastic film and integrate the battery material industry chain.
Mingguan New Materials: Independently developed and certified by multiple battery manufacturers.
Foster: Leading the photovoltaic film industry, entering the aluminum-plastic film field.
02 Core Technology
Aluminum plastic film is the key packaging material for soft pack batteries, which needs to meet the three core requirements of high barrier properties, electrolyte corrosion resistance, and heat sealing performance. The technical difficulties focus on the four layer structure:
1. Outer layer (nylon layer)
Function: Mechanical protection and moisture resistance.
Technical difficulty: Scratch resistance, electrolyte penetration resistance, requiring special coating treatment.
2. Intermediate layer (aluminum foil)
Core barrier: thickness of about 30-40 μ m.
Technical difficulties:
Surface treatment: Aluminum foil needs to be cleaned and passivated (chromate/chromium free treatment) to enhance corrosion resistance.
Pinhole control: Defects in aluminum foil cause water and oxygen infiltration, requiring precision rolling technology (led by Japanese companies).
3. inner layers (CPP layer)
The most critical technology: direct contact with electrolyte, requiring corrosion resistance and heat sealing properties.
Technical difficulties:
Modified CPP: Adding special functional groups (such as maleic anhydride) to enhance electrolyte resistance.
Heat sealed window: Ensure packaging strength (>20N/15mm) and prevent cracking.
4. Adhesive layer
Technical difficulty: The adhesive needs to withstand both electrolyte and high temperature (above 150 ℃), and Japanese companies have high patent barriers.
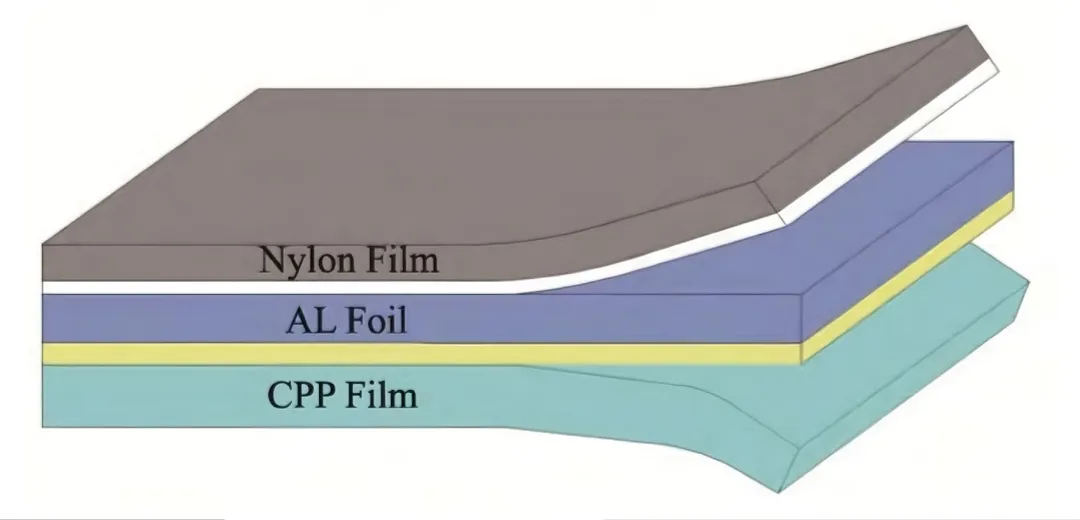
Schematic diagram of aluminum-plastic film structure
Comparison of technical routes
Process characteristics: CPP and aluminum foil are directly hot pressed and bonded with adhesive after melting
Advantages: Strong electrolyte resistance, good deep penetration performance, high barrier properties, and smooth appearance
Disadvantage: Low heat sealing strength, slightly weaker resistance to electrolyte
Representing enterprises DNP, Showa Denko, Showa Denko&Chinese Enterprises
03 Localization Progress and Challenges
Progress: Chinese companies have achieved technological breakthroughs through acquisitions (such as Newlun's acquisition of T&T) or self research (Daoming, Zijiang), replacing the consumer electronics field and accelerating penetration into the power battery field.
Challenge:
1. Raw material dependence: High end aluminum foil (Japan Toyo, UACJ) and CPP particles (Japan Toray) still rely on imports.
2. Process stability: There is still a gap between Japan and Japan in terms of pinhole rate and water oxygen permeability (≤ 0.01 g/m ² · day).
3. certification cycles: Customer certification for power batteries takes 2-3 years, with a high threshold.